Introduction to Microsoft LLMLingua
Accelerating LLMs with Advanced Prompt Compression
Introduction
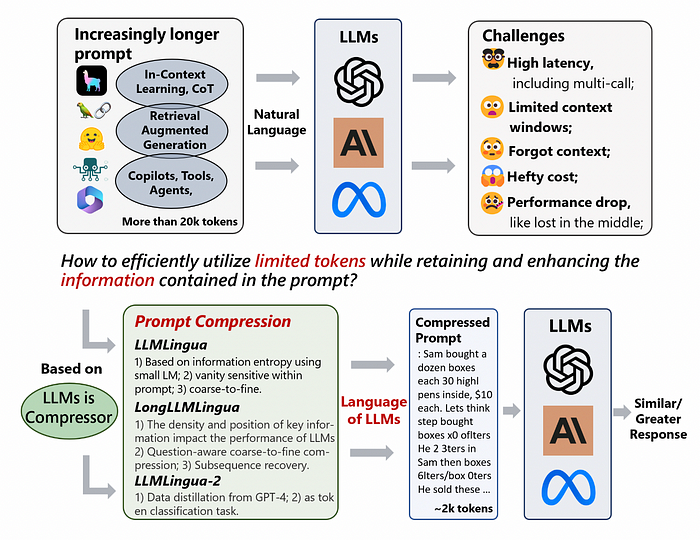
Large Language Models (LLMs) have become central to numerous AI applications, from natural language processing to complex reasoning tasks. Despite their remarkable capabilities, LLMs face challenges like limited prompt size and context windows, which constrain their ability to process and generate comprehensive responses. Enter LLMLingua and its advanced variant LongLLMLingua — innovative frameworks designed to enhance LLM efficiency by refining and compressing input data, thus overcoming these inherent limitations. This article delves into the architecture, mechanisms, and future potential of LLMLingua.
What is LLMLingua?
LLMLingua is a novel framework engineered to optimise the interaction between users and LLMs by addressing one of the core challenges: context window limitations. In LLMs, the context window defines the amount of information that can be processed at once. LLMLingua mitigates this bottleneck by systematically refining and compressing input data, making it more digestible for LLMs without losing essential content.
Imagine teaching a group of aspiring chefs how to prepare a gourmet meal. Instead of overwhelming them with every detail, you’d break down the instructions into clear, concise steps, focusing on the crucial techniques and ingredients. LLMLingua operates similarly, acting as a skilled AI chef. It prepares information in a way that LLMs, like AI apprentices, can easily digest and master.
Rather than bombarding LLMs with raw data, which can lead to slow processing and limited performance, LLMLingua meticulously trims and refines this information, ensuring the models receive only the essential components, much like a chef using just the right spices to enhance a dish.
Key Features of LLMLingua:
- Data Compression: LLMLingua compresses input data, reducing its size while retaining critical information. This allows LLMs to process more significant amounts of data within their context window.
- Information Refinement: The framework refines the data by removing redundancies and emphasising the most relevant details, enhancing the clarity and focus of the input.
- Scalability: LLMLingua is adaptable to various tasks and can be scaled to handle different data types and volumes, making it versatile across multiple applications.
How LLMLingua Works
LLMLingua operates through a multi-step pipeline designed to enhance the efficiency of LLMs:
- Data Preprocessing: Input data is first preprocessed to identify and filter out irrelevant or redundant information. This step ensures that only the most pertinent details are passed on to the next stage.
- Contextual Compression: The refined data is then compressed into a format that maximises the amount of information that fits within the LLM’s context window. This step involves advanced encoding techniques that preserve semantic meaning while reducing data size.
- Input Optimisation: The compressed data is further optimised to align with the specific requirements of the LLM. This includes adjusting the format, structure, and even linguistic nuances to ensure the LLM can process the input effectively.
- Model Interaction: The optimised data is fed into the LLM, which can now handle more extensive and complex inputs within its context window, leading to improved performance in tasks such as summarisation, translation, and question-answering.
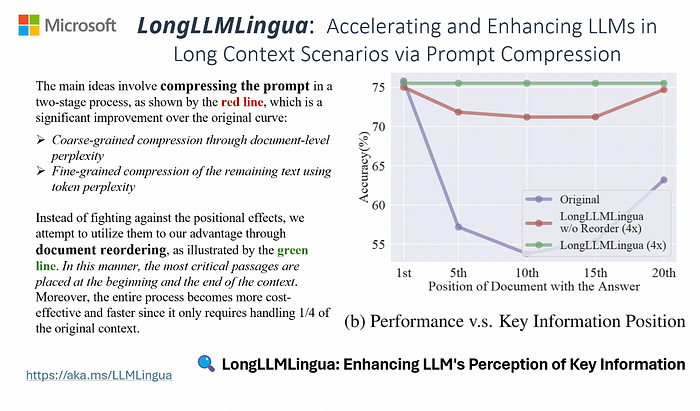
LongLLMLingua: Extending Capabilities
While LLMLingua addresses the limitations of standard LLMs, LongLLMLingua takes it a step further by enabling LLMs to handle even longer sequences of text. This advanced version builds on LLMLingua’s foundational techniques but introduces additional layers of compression and refinement.
Ever encountered the token limit when asking ChatGPT to summarise lengthy texts? Frustrated with ChatGPT forgetting previous instructions after extensive fine-tuning? Experienced high costs using GPT3.5/4 API for experiments despite excellent results? While Large Language Models like ChatGPT and GPT-4 excel in generalisation and reasoning, they often face challenges like prompt length limits and prompt-based pricing schemes.
Now you can use LLMLingua, LongLLMLingua, and LLMLingua-2!
These tools offer an efficient solution to compress prompts by up to 20x, enhancing the utility of LLMs.
- Cost Savings: Reduces both prompt and generation lengths with minimal overhead.
- Extended Context Support: Enhances support for longer contexts, mitigates the “lost in the middle” issue, and boosts overall performance.
- Robustness: No additional training is needed for LLMs.
- Knowledge Retention: Maintains original prompt information like ICL and reasoning.
- KV-Cache Compression: Accelerates inference process.
- Comprehensive Recovery: GPT-4 can recover all key information from compressed prompts.
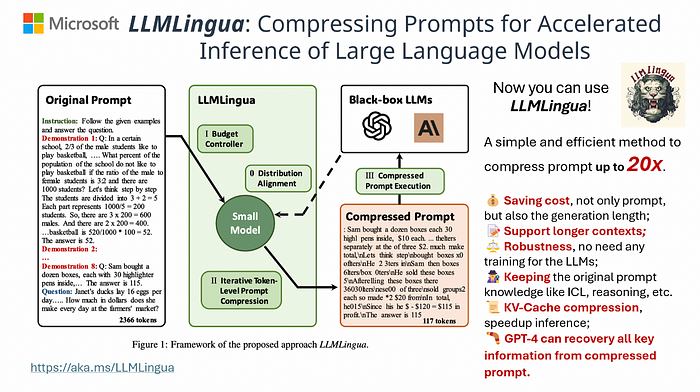
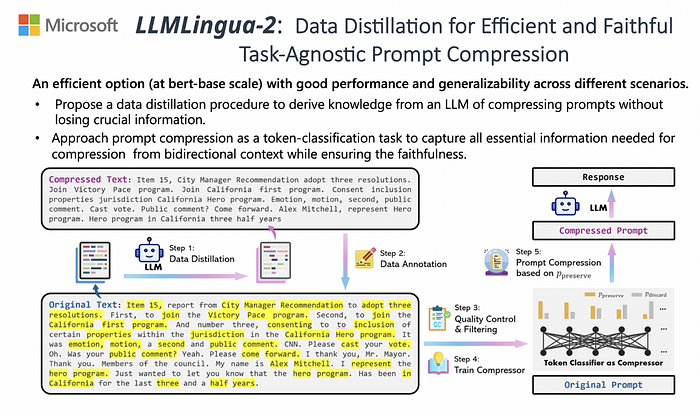
Practical demonstration of LongLLMLingua approach for Prompt Compression
The objective of this project is to efficiently retrieve, compress, and process large textual data from a Wikipedia article using advanced language models and prompt engineering techniques. By leveraging tools like LLMLingua, the project aims to handle and compress extensive context data to fit within the token limitations of models like GPT-3.5, ensuring that the most relevant information is retained. This approach enables the generation of accurate and concise answers to specific questions, even when dealing with extensive and complex datasets, thus optimising the utility of large language models for question-answering tasks. Google Colab has been used for this demonstration.
Note: For this project, OpenAI subscription is needed to use OpenAI API Key. It’s very affordable and easy to get started. Here’s how you can proceed:
For more details visit OpenAI Documentation.
- Installing Required Libraries
!pip install cohere
!pip install llama_index
!pip install openai
!pip install llmlingua
!pip install accelerate
!pip install --force-reinstall llama-index
!pip install wikipedia2. Loading Wikipedia Data
# Import necessary tools
from llama_index.core import (
VectorStoreIndex, # Allows working with vector stores
download_loader, # Downloads loaders for loading data
load_index_from_storage, # Loads indices from storage
StorageContext, # Manages storage contexts
)
WikipediaReader = download_loader("WikipediaReader")
loader = WikipediaReader()
documents = loader.load_data(pages=['Mexican–American_War'])3. Setting Up OpenAI API Key
Getting an OpenAI API Key:
Go to OpenAI, sign up/login, and choose a subscription plan if you already don’t have a paid plan. Get API Key: After subscribing, generate your API key from your account dashboard. Copy it and paste it when the output of the below code asks for it.
## Your own openai key will be needed.
import openai
openai.api_key = 'API_KEY'4. Creating and Using a Vector Store Index
## Your own openai key will be needed.
index = VectorStoreIndex.from_documents(documents)
retriever = index.as_retriever(similarity_top_k=3)
question = "What were the main outcomes of the war"
contexts = retriever.retrieve(question)
context_list = [n.get_content() for n in contexts]
context_list5. Generating a Response with OpenAI’s GPT-3.5 Comparison
# The response from original prompt
from llama_index.llms.openai import OpenAI
from llama_index.core.prompts.prompts import PromptTemplate
llm = OpenAI(model="gpt-4")
template = (
"We have provided context information below. \n"
"---------------------\n"
"{context_str}"
"\n---------------------\n"
"Given this information, please answer the question: {query_str}\n"
)
qa_template = PromptTemplate(template)
# you can create text prompt (for completion API)
prompt = qa_template.format(context_str="\n\n".join(context_list), query_str=question)
response = llm.complete(prompt)
print(str(response))6. Setting Up LLMLingua and Postprocessing Nodes
!pip install llama-index-postprocessor-longllmlingua
# Setup LLMLingua
from llama_index.core.query_engine import RetrieverQueryEngine
from llama_index.core.response_synthesizers import CompactAndRefine
from llama_index.postprocessor.longllmlingua import LongLLMLinguaPostprocessor
node_postprocessor = LongLLMLinguaPostprocessor(
instruction_str="Given the context, please answer the final question",
target_token=300,
rank_method="longllmlingua",
additional_compress_kwargs={
"condition_compare": True,
"condition_in_question": "after",
"context_budget": "+100",
"reorder_context": "sort", # enable document reorder,
"dynamic_context_compression_ratio": 0.3,
},
)
retrieved_nodes = retriever.retrieve(question)
synthesizer = CompactAndRefine()7. Applying Postprocessing and Compression
from llama_index.core.schema import QueryBundle
new_retrieved_nodes = node_postprocessor.postprocess_nodes(
retrieved_nodes, query_bundle=QueryBundle(query_str=question)
)
original_contexts = "\n\n".join([n.get_content() for n in retrieved_nodes])
compressed_contexts = "\n\n".join([n.get_content() for n in new_retrieved_nodes])
original_tokens = node_postprocessor._llm_lingua.get_token_length(original_contexts)
compressed_tokens = node_postprocessor._llm_lingua.get_token_length(compressed_contexts)
print(compressed_contexts)
print()
print("Original Tokens:", original_tokens)
print("Compressed Tokens:", compressed_tokens)
print("Compressed Ratio:", f"{original_tokens/(compressed_tokens + 1e-5):.2f}x")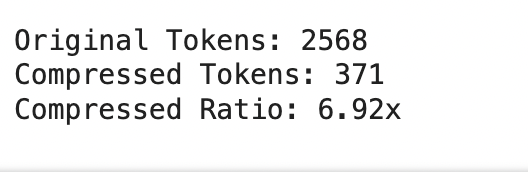
8. Synthesising the Final Response
response = synthesizer.synthesize(question, new_retrieved_nodes)
print(str(response))Results of Reasoning and ICL Scenarios
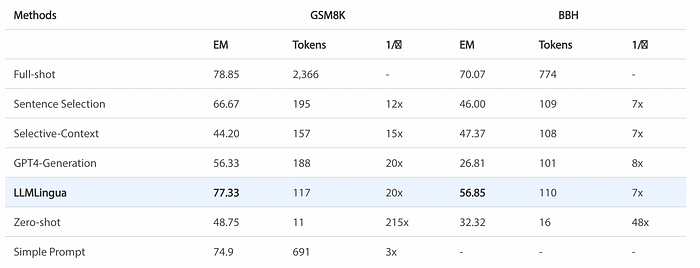
LLMLingua was tested originally in various scenarios, including reasoning, in-context learning (ICL), summarisation, and dialogue. The results in the GSM8K and Big-bench Hard Benchmark are listed below. Notably, within the GSM8K, LLMLingua was able to retain the reasoning capabilities of LLMs at a 20x compression ratio, with only a 1.5% loss in performance.
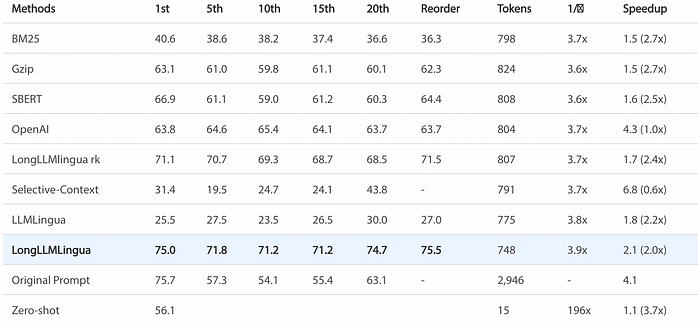
Results of RAG scenarios (Multi-document QA)
LLMLingua is tested across a range of scenarios, such as multi-document QA, coding, retrieval-based tasks, multi-hop QA, summarisation, and ranking, with the NQ multi-document QA results highlighted below. Notably, LongLLMLingua effectively mitigates the ‘lost in the middle’ issue, achieving up to a 21.4% improvement at 4x compression and achieving a 2.1x acceleration in end-to-end latency.
Key Advantages of LongLLMLingua:
- Extended Context Handling: LongLLMLingua allows LLMs to process much larger inputs, extending the effective context window and enabling more detailed and comprehensive outputs.
- Enhanced Accuracy: By preserving more context, LongLLMLingua improves the accuracy of LLM-generated responses, particularly in tasks that require understanding long documents or conversations.
- Task-Specific Optimisation: LongLLMLingua can be tailored for specific use cases, such as legal document analysis or academic research, where large volumes of text need to be processed without losing contextual integrity.
Real-World Applications
The impact of LLMLingua and LongLLMLingua is evident in various domains:
- Legal Tech: These frameworks are used to compress and analyse extensive legal documents, enabling LLMs to provide accurate summaries and insights.
- Healthcare: In the medical field, LLMLingua helps in processing patient records and research papers, aiding in diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Content Generation: For content creators, LLMLingua enhances the ability of LLMs to generate coherent and contextually accurate long-form articles, reports, and creative writing.
Conclusion
LLMLingua and LongLLMLingua represent significant advancements in the field of large language models, addressing one of the most pressing challenges: the limitation of context windows. By refining and compressing input data, these frameworks enable LLMs to process larger and more complex datasets, opening new possibilities in AI-driven tasks. As LLM technology continues to evolve, LLMLingua and LongLLMLingua will likely play a crucial role in expanding the capabilities and applications of these powerful models.
References
- Hugging Face, “LLMLingua by Microsoft,” [Online]. Available: https://huggingface.co/spaces/microsoft/LLMLingua. [Accessed: Aug. 15, 2024].
- LLMLingua. Microsoft GitHub Repository. https://github.com/microsoft/LLMLingua (accessed Aug. 13, 2024).
- Microsoft Research, “LLMLingua,” Microsoft, [Online]. Available: https://www.microsoft.com/en-us/research/project/llmlingua/. [Accessed: Aug. 13, 2024].
Catch the latest version of this article over on Medium.com. Hit the button below to join our readers there.