OpenAI Canvas and DevDay: Advancing AI Collaboration with Voice Realtime API, Model Distillation, and More
Explore OpenAI’s latest tools and features — Canvas, Realtime API, Prompt Cache, Visual Fine-Tuning
Introduction
OpenAI recently introduced a new feature called Canvas, which is designed to provide ChatGPT users with a more powerful writing and coding collaboration experience. Canvas is a newly crafted interface that offers an independent workspace beyond the usual ChatGPT dialogue, built on the latest GPT-4o model to support more complex writing and coding projects.
Canvas focuses on two main categories: writing and coding. On the writing side, Canvas offers editing suggestions, adjustable text length, readability level options, and the ability to add final touches, including emojis. On the coding side, Canvas provides code review, annotation and logging, bug fixing, and the capability to convert code into other programming languages such as JavaScript or Python. These features allow users to co-create and refine ideas with AI, making collaboration more seamless and effective.
In essence, Canvas introduces a novel way for users and AI to work side by side — not just through simple dialogue, but as genuine collaborators. This helps users precisely address and optimise content within the project’s context, marking yet another step by OpenAI towards enhancing productivity with AI, aiming for a more integrated and smooth collaborative experience.
At the recent DevDay, OpenAI also announced five major innovations: Realtime API, Prompt Cache, Model Distillation, Visual Fine-Tuning, and New Playground Features. These updates signal a shift in OpenAI’s strategic focus towards infrastructure and the developer ecosystem, rather than solely competing in the end-user AI application market.
Compared to last year’s grand reveal, this year’s DevDay was more understated, focusing on incremental improvements to existing AI tools and API suites while showcasing enhanced developer capabilities and community stories. Here’s a brief overview of the five updates:
- Realtime API: Offers developers a near real-time “speech-to-speech” experience, with six voice options provided by OpenAI.
- Prompt Cache: Similar to the feature introduced by Anthropic earlier, this allows developers to cache common contexts between API calls, reducing costs and improving latency.
- Model Distillation: Developers can fine-tune smaller models (such as GPT-4o mini) using larger models like o1-preview and GPT-4o.
- Visual Fine-Tuning: Combines images and text to fine-tune GPT-4o applications, significantly enhancing the model’s visual understanding.
- New Playground Features: Offers a new framework and usage options for prompts, along with breakthroughs in structured output, making development easier than ever.
Canvas: Collaborate Side-by-Side with ChatGPT
Canvas is a new feature of ChatGPT that provides an independent workspace, allowing users to interact with ChatGPT in a more intuitive and flexible way. Built on OpenAI’s latest GPT-4o model, Canvas overcomes the limitations of traditional chat windows for handling complex tasks. Whether it’s writing or coding, this new collaborative approach offers an enhanced experience.
Currently, Canvas is in its testing phase and can be manually selected across all models. Plus users have immediate access without any wait, while OpenAI plans to eventually roll it out to all free users. With Canvas, you can do research, write code, draft emails, and most importantly, brainstorm creatively alongside ChatGPT.

In Canvas mode, it’s no longer just about having a simple conversation. Instead, users can refine, rework, and organise the generated content — essentially transforming the process into something akin to a content or code editor.
For instance, if you upload a file and ChatGPT generates some content, you’ll notice an “Edit” button in the bottom right corner of the interface, allowing you to take full control of the generated output.

This button reveals five features, which include:
- Suggest edits
- Adjust the length
- Reading level
- Add final polish
- Add emojis
For example, with the “Suggest edits” feature, you can simply select the portion of text you want to modify, then click “Apply” to have the content automatically regenerated.

You can also “highlight” the article title and have it “reworked” to your requirements, with fine-tuning options available.

You can also highlight specific sections to draw ChatGPT’s attention, allowing the model to provide in-line feedback and suggestions while considering the overall project context.

So, what else can you do with Canvas? Let’s continue exploring.
Writing with ChatGPT
Earlier, we showcased the “Edit” feature within Canvas writing. Now, let’s take a look at the “Adjust the Length” option.
As the name suggests, this feature allows you to adjust the length of the document, making it either shorter or longer. There are five settings available: Current Length, Longer, Longest, Shorter, and Shortest.

Once you select the desired length, ChatGPT will adjust the entire text, modifying it word by word and paragraph by paragraph.

The “Change Reading Level” feature is quite impressive, offering six levels: Kindergarten, Middle School, Current Level, High School, College, and Graduate.
Simply select the desired reading level, and ChatGPT will adjust the entire text accordingly.

The “Add Final Polish” feature makes comprehensive edits to the entire text, including checking grammar, clarity, and consistency.

The “Add Emojis” feature is quite fun — it lets you add emojis to your text, making the content more lively and engaging.
For example, one user shared their creative result:

Coding with ChatGPT
In addition to writing, Canvas also offers a coding feature, which includes the following five capabilities:
- Review code
- Add logs
- Add comments
- Fix bugs
- Port to a language

For example, let’s give ChatGPT a request:
Help me write an API web server in Rust.

In Canvas, you can highlight a specific code snippet and request modifications according to your requirements.

For specific details, you also have the option to manually make changes.

For features like code review, adding logs, adding comments, and fixing bugs, a single click allows you to make global changes.
Notably, the Change Programming Language feature currently offers options including JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, Java, C++, and PHP.

Making AI the Ultimate Collaborator
For Canvas, OpenAI has implemented over 20 automated internal evaluations to measure progress, utilising novel synthetic data generation techniques — such as extracting outputs from OpenAI o1-preview — to conduct post-training on the model for its core behaviours.
The advantage of this approach is the ability to quickly address writing quality and new user interaction issues without relying on manually generated data.
A key challenge is defining when to trigger Canvas. The model needs to be sensitive enough to identify tasks requiring detailed review or modification, like “write a blog post about the history of coffee beans,” while avoiding unnecessary activations for more general tasks, such as “help me create a new dinner recipe,” which might not require Canvas.

For writing and coding tasks, we improved correctly triggering the canvas decision boundary, reaching 83% and 94% respectively compared to a baseline zero-shot GPT-4o with prompted instructions.
The second challenge involves adjusting the model’s editing behaviour once Canvas is triggered, particularly deciding when to make targeted edits instead of rewriting the entire content.
The model is trained to favour targeted edits, especially when the user explicitly selects text. As the model continues to evolve, its ability to handle these nuanced editing tasks is also improving.

For writing and coding tasks, we prioritised improving canvas-targeted edits. GPT-4o with canvas performs better than a baseline prompted GPT-4o by 18%.
Lastly, training the model to generate high-quality code comments also requires a detailed iterative process. This evaluation differs from the previous cases. While determining whether Canvas was triggered or whether targeted edits were made can be easily automated, assessing the quality of code comments is more challenging to automate, leading the team to opt for manual evaluation.
Compared to the baseline model, the integration of Canvas improved GPT-4o’s comment accuracy by 30% and overall quality by 16%. This indicates that training with synthetic data significantly enhances the model’s response quality and behaviour, compared to zero-shot prompts with detailed instructions.

Human evaluations assessed canvas comment quality and accuracy functionality. Our canvas model outperforms the zero-shot GPT-4o with prompted instructions by 30% in accuracy and 16% in quality.
A developer described the Canvas interface as a game changer. They recently used Canvas with ThreeJS to create a tesseract/Hypercube visualisation tool and mentioned how much they enjoy the unified UX for chatting, live reviews and watching GPT-4o work its magic on code — all in one place, always relevant.


Realtime Multimodal Conversation API: The Era of AI Voice Applications Has Arrived!
OpenAI’s newly launched Realtime API is currently in public beta.
This new product allows developers to create low-latency, multimodal experiences, particularly for voice-to-voice applications.
This means developers can now start adding ChatGPT’s “voice controls” to their apps.
To showcase the API’s potential, OpenAI demonstrated an updated version of Wanderlust — a “travel planning” app originally presented at last year’s event. With the Realtime API, users can interact with the app directly, planning trips in a natural, conversational manner. The system even supports interruptions, mimicking the pauses and nuances of human conversation.
While the travel planning app is just an example, the Realtime API opens up a wide range of possibilities for voice applications across various industries.
From customer service to education and assistive tools, developers now have a powerful new resource for creating more intuitive, responsive AI-driven experiences.
The Realtime API essentially simplifies the process of building voice assistants and other conversational AI tools, eliminating the need to piece together multiple models for transcription, inference, and text-to-speech conversion.
Early adopters of the Realtime API, such as Healthify — a nutrition and fitness guidance app — and Speak, a language learning platform, have already integrated the API into their products. These implementations demonstrate the potential of the API to create more natural, engaging user experiences in fields like healthcare and education.
Though the Realtime API is not cheap ($0.06 per minute for audio input, $0.24 per minute for audio output), it still represents a significant value proposition for those looking to develop voice-based applications.
Prompt Cache: A Major Budget Saver for Developers
The “Prompt Cache” feature is designed to reduce costs and latency for developers.
The system automatically applies a 50% discount to tokens that the model has recently processed, which can lead to substantial savings for applications that frequently reuse context.
The significant reduction in costs opens up major opportunities for startups and large enterprises to explore new applications that were previously unattainable due to budget constraints.
At the 2024 OpenAI DevDay, the pricing chart showed a significant reduction in the cost of using AI models. Cached input tokens can save up to 50% compared to non-cached tokens across various GPT models. The new o1 model further highlights its advanced capabilities.
This also involves structured prompts, where caching hits are only possible when the prefixes of prompts match exactly. To take full advantage of caching, it’s necessary to place static content (such as instructions and examples) at the beginning of the prompt and put variable content (such as user-specific information) at the end. This also applies to images and tools, which must remain consistent between requests.
Model Distillation: Making AI Model Training More Efficient
Perhaps the most transformative change at DevDay was the introduction of “Model Distillation.” This integrated workflow allows developers to use outputs from advanced models like o1-preview and GPT-4o to improve the performance of more efficient models like GPT-4o mini.
In everyday training, larger AI models (such as o1-preview and GPT-4o) can be used to fine-tune smaller models (like GPT-4o mini). This approach enables small companies to utilise capabilities similar to advanced models without incurring the same computational costs.
It bridges the longstanding gap in the AI industry between cutting-edge, resource-intensive systems and more accessible but less powerful systems. For instance, a small health tech startup developing an AI diagnostic tool for rural clinics can use model distillation to train a compact model that runs on a standard laptop or tablet, capturing much of the diagnostic capability of larger models. This brings advanced AI capabilities to resource-limited settings, potentially improving healthcare outcomes in underserved areas.
Visual Fine-Tuning: The New Frontier of Visual AI
Another major update is the introduction of visual fine-tuning for OpenAI’s latest large language model, GPT-4o. This feature allows developers to customise the model’s visual understanding using both images and text.
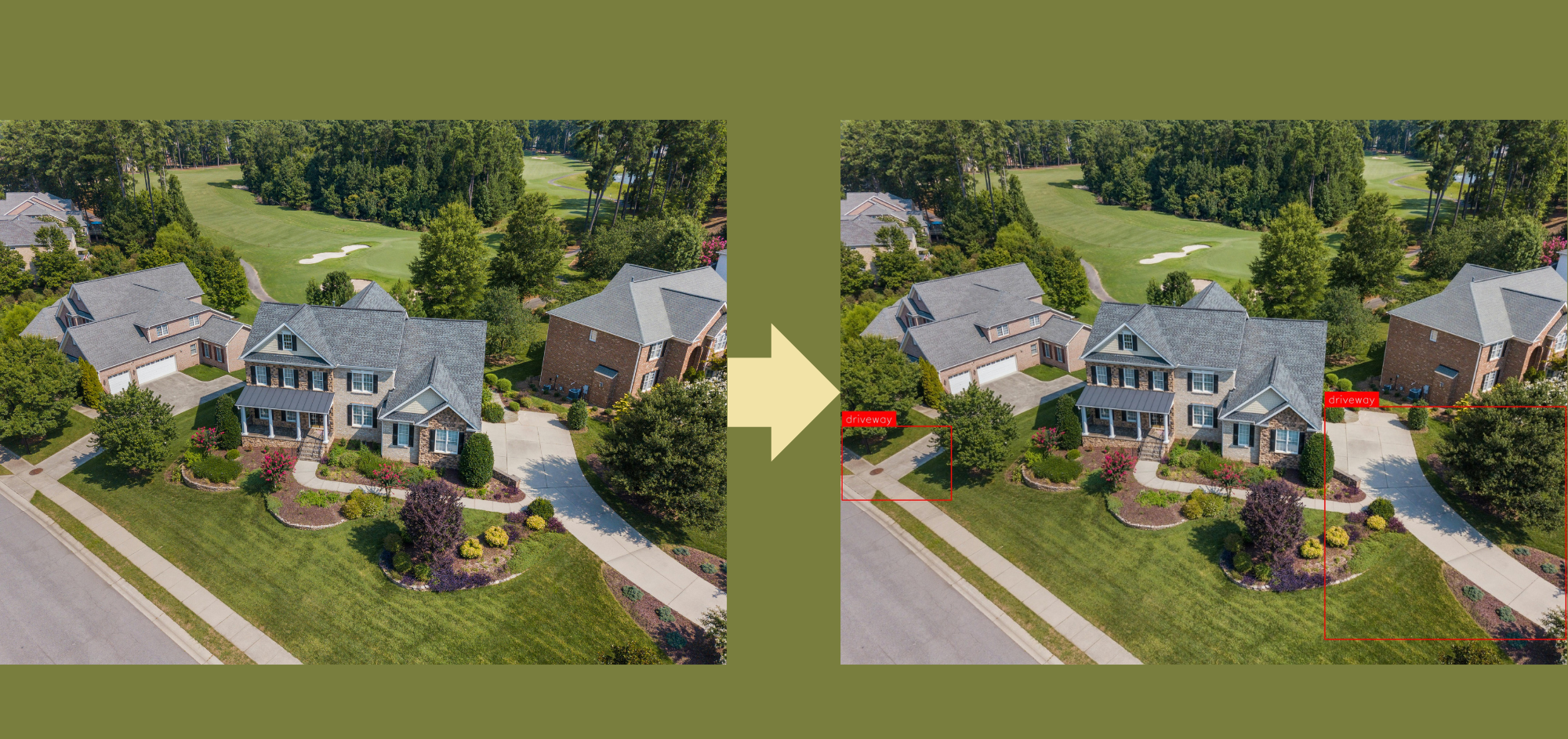
The impact of this update is profound, with potential applications in areas such as autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, and visual search functionalities. According to OpenAI, Grab, a leading food delivery and ride-hailing company in Southeast Asia, has utilised this technology to improve its mapping services. Reportedly, with only 100 examples, Grab increased lane count accuracy by 20% and speed sign recognition accuracy by 13%.
This real-world application demonstrates the potential of visual fine-tuning, showing that using small batches of visual training data can significantly enhance AI services across industries.
Gathering information in a “pure visual” manner through “seeing” will greatly expand future application scenarios. Combined with “real-time voice interaction,” OpenAI’s advances in information processing and interaction create possibilities for a new wave of applications.
Envisioned scenarios include assisting people with visual or hearing impairments, recognising emergencies and hazards through visual identification, and calling for help automatically.
New Playground Features: Building a Sustainable AI Ecosystem
More explanations have been provided on the structured framework for prompts and other usages. Parts of this information were allegedly leaked a day earlier, including the so-called “System Prompts.”
The key elements include: “Understand the task: Grasp the main objectives, goals, requirements, constraints, and expected outputs.”
- Minimal Changes: If an existing prompt is provided, only make simple improvements if possible. For more complex prompts, enhance clarity and add missing elements without changing the original structure.
- Reasoning Before Conclusion: Encourage reasoning steps before arriving at any conclusion. Attention! If the user provides an example where reasoning follows, REVERSE the order! Never begin examples with a conclusion!
- Reasoning Order: Highlight the reasoning parts of the prompt and conclusion sections (specifically named fields). For each, determine the ORDER in which to do so and whether a reversal is needed.
- Conclusion, Classification, or Outcome: These should always come last.
Conclusion
OpenAI’s Canvas and recent DevDay innovations represent a major step forward in AI collaboration, offering developers powerful tools like the Realtime API, Prompt Cache, Model Distillation, Visual Fine-Tuning, and Playground features. These advancements make AI more accessible, enhance productivity in writing and coding, and support industries like healthcare and assistive technology. By bridging human creativity with AI efficiency, OpenAI aims to foster a sustainable ecosystem that empowers developers and creates real-world impact.
References
- Openai.com. (2024). Introducing canvas. https://openai.com/index/introducing-canvas/.
- X (formerly Twitter). (2024). x.com. https://x.com/karinanguyen_/status/1841889811931791642.
Catch the latest version of this article over on Medium.com. Hit the button below to join our readers there.