What is Multimodal AI?
Exploring the Interdisciplinary Nature of Multimodal AI
Introduction
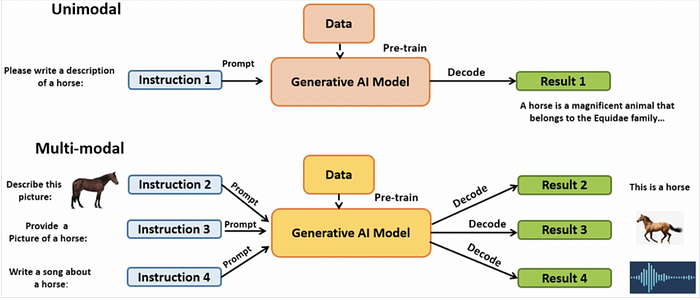
Multimodal AI is revolutionising the way businesses interpret and utilise data by integrating multiple forms of information — such as text, audio, and visual input — to create more nuanced and effective AI solutions. At its core, multimodal AI works by combining these different data types to provide a holistic understanding of a given context, making it far superior to unimodal AI, which relies on a single data type. The benefits of multimodal AI are substantial; companies can unlock insights across diverse datasets, enhancing decision-making and driving innovation in various fields, from healthcare to marketing. For instance, healthcare applications of multimodal AI can analyse patient records and imaging data simultaneously, leading to improved diagnostics. However, implementing multimodal AI comes with its challenges, including the need for robust data infrastructure and advanced algorithms that can handle complex integrations. Organisations looking to leverage multimodal AI can explore various top tools and platforms and consider custom development solutions to fit their specific needs. Ultimately, with the right strategies and support, businesses can effectively harness the power of multimodal AI to gain a competitive edge in today’s data-driven landscape.
Multimodal AI in depth
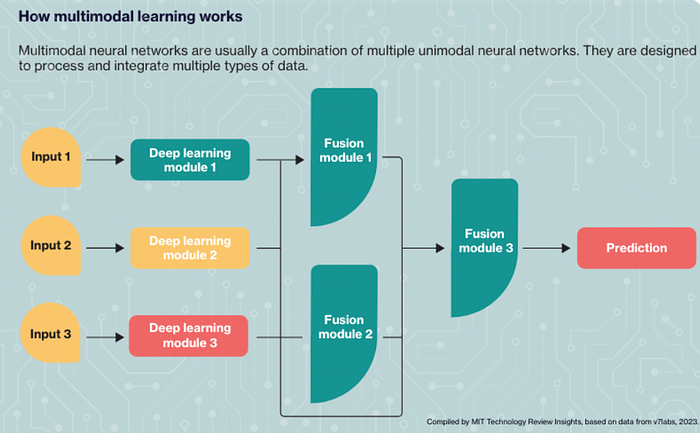
Multimodal AI is an interdisciplinary field that combines different modalities of data — text, image, audio, and video — to build AI systems capable of understanding and generating content across these formats. Unlike unimodal AI, which focuses on a single type of data, multimodal AI enables a more human-like interaction by leveraging multiple data types, much like how humans use their senses to perceive the world. For example, GPT-4, an advanced multimodal model, can process text and images simultaneously to provide a more nuanced response to user inputs, such as generating a description from an image or understanding context better through combined modalities. But what makes multimodal AI unique is the ability to combine and fuse the outputs from these different models.
There are three primary components:
- Input modules: These are unimodal neural networks that individually receive and process different types of data, such as text, audio, and images.
- Fusion modules: These modules extract relevant information from each modality, integrating and aligning the data to pinpoint the most significant details.
- Output modules: These modules generate the final result, decision, or prediction for the user based on the data that has been processed and integrated earlier in the system.
The main multimodal fusion component merges information from various inputs, addressing any conflicts or ambiguities to create a cohesive multimodal output. This fusion component can integrate data from different modalities using methods like deep learning neural networks or rule-based systems. It can also utilise contextual information to better interpret the user’s intent, resulting in more accurate and coherent responses.
Core Concepts of Multimodal AI
Multimodal generative AI models enhance the complexity of leading Large Language Models (LLMs) by using a neural architecture known as a Transformer. Developed by Google researchers, transformers utilise an encoder-decoder structure and an attention mechanism, which allows them to process data more efficiently. To create a comprehensive and accurate understanding of different types of data, multimodal AI relies on data fusion techniques. These techniques integrate various data types to improve prediction accuracy by combining the complementary information from each modality. Data fusion can be performed at different stages of processing, and is generally categorised into three types:
- Early fusion: This technique involves encoding multiple modalities into a model to form a common representation space, resulting in an output that encapsulates the semantic information from all modalities.
- Mid fusion: This method combines different modalities at various preprocessing stages by incorporating special layers in the neural network specifically designed for data fusion.
- Late fusion: This approach uses separate models to process each modality and then combines their outputs in a new algorithmic layer. There isn’t a one-size-fits-all data fusion technique for every scenario. The choice of technique depends on the specific multimodal task, often requiring experimentation to identify the most effective AI pipeline.
The Role of Large Language Models in Multimodal AI
LLMs are at the core of many multimodal AI advancements. These models, with their vast number of parameters and deep learning capabilities, serve as the backbone for understanding and generating human-like text, which is crucial in multimodal settings.
1. Text-to-Image Generation
LLMs contribute significantly to text-to-image generation tasks. They can generate descriptive captions for images based on textual input, enhancing applications like automated image captioning. By understanding the semantics of text, LLMs can describe images in ways that align closely with human interpretation.
2. Language-Vision Pretraining
LLMs can be pretrained on both text and image data, allowing them to learn the intricate relationships between language and visual content. This cross-training improves performance on tasks that involve both modalities, such as visual question answering and image-based search.
3. Multimodal Understanding
One of the most transformative roles of LLMs in multimodal AI is bridging the gap between text and other data types. For instance, multimodal chatbots utilise LLMs to interpret user inputs that include both text and images, providing richer, more context-aware responses.
4. Multimodal Representation Learning
LLMs can extract joint representations of text and images, which are essential for applications like information retrieval and recommendation systems. By learning these combined representations, LLMs help improve the accuracy and relevance of search results and recommendations, enhancing user experiences.
Applications of Multimodal AI
The integration of LLMs into multimodal AI has expanded its applications across various industries:
- Augmented Generative AI: Multimodal models enhance the user experience by accepting inputs in multiple formats and generating diverse outputs. This capability is particularly valuable in content creation, where AI can assist in generating text, images, and even videos from combined inputs.
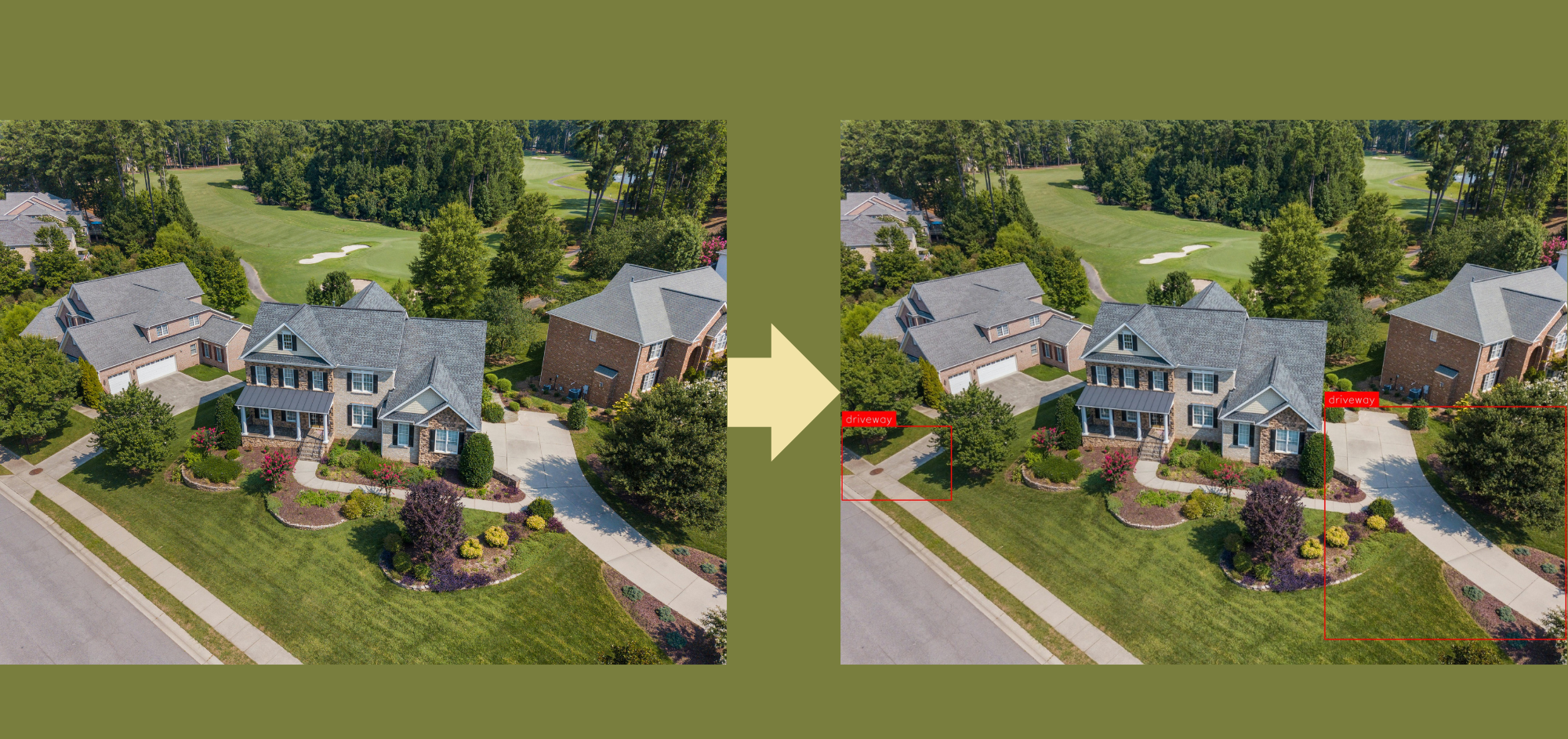
- Autonomous Vehicles: Self-driving cars rely on multimodal AI to process data from various sensors (cameras, LIDAR, etc.) to understand their surroundings and make real-time decisions.
- Biomedicine: In healthcare, multimodal AI can analyse diverse data sources, such as medical records, imaging data, and genetic information, to provide comprehensive diagnostics and treatment recommendations.
- Earth Science and Climate Change: Multimodal AI helps in analysing satellite images, ground sensor data, and other environmental measurements to monitor climate change and predict extreme weather events.
Challenges and Ethical Considerations in Multimodal AI
While the potential of multimodal AI is immense, integrating LLMs comes with challenges:
- Data Fusion and Cross-Modal Understanding: Combining different data types seamlessly is complex and requires robust models that can align disparate modalities without losing context.
- Bias and Fairness Issues: LLMs are susceptible to biases present in their training data. When extended to multimodal AI, these biases can affect the fairness and inclusivity of the resulting applications.
- Privacy and Security Concerns: The use of multimodal data, which often includes sensitive information, necessitates stringent measures to protect privacy and ensure data security.
- Environmental Impact: Training and deploying large-scale LLMs in multimodal AI require significant computational resources, raising concerns about energy consumption and sustainability.
Future Trends and Developments
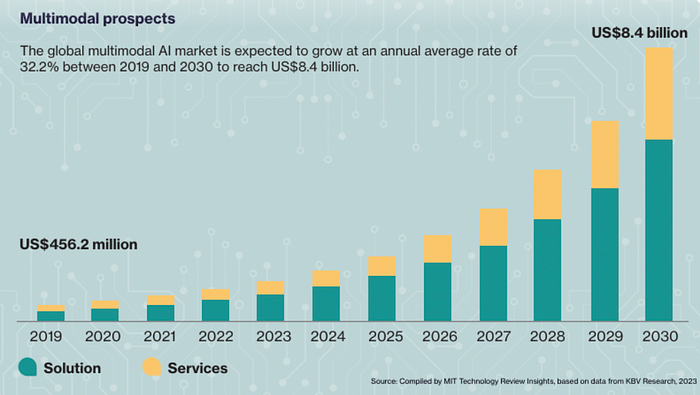
The global multimodal AI market is expected to expand rapidly in the coming years. MIT Technology Review Insights predicts that the market for multimodal AI solutions and services could increase at an average annual rate of 32.2% until 2030, potentially reaching a total value of $8.4 billion. Utilising multimodal generative AI (GenAI) can offer substantial advantages for businesses across various industries, enhancing front-office services by improving customer experiences and optimising back-office operations through increased efficiency.
The future of multimodal AI, powered by LLMs, looks promising, with several exciting trends on the horizon:
- Enhanced Multimodal Models: Continued research will likely lead to the development of more sophisticated LLMs capable of better integrating and interpreting multiple data types.
- New Use Cases: As multimodal AI becomes more advanced, new applications will emerge, such as immersive storytelling and personalised education, where AI can tailor content to individual learning styles using text, images, and videos.
- Integration with Other AI Technologies: The convergence of LLMs with other AI technologies, like reinforcement learning and computer vision, will create more versatile and intelligent systems, potentially revolutionising fields like robotics and autonomous navigation.
Conclusion
Large Language Models have transformed AI by enabling machines to understand and generate human-like text. Their role in multimodal AI is equally groundbreaking, as they enhance the integration of different data types, making AI systems more versatile, comprehensive, and human-like. However, with this advancement comes the responsibility to address ethical concerns, biases, and environmental impacts to ensure a fair and sustainable future for AI. As we continue to push the boundaries of AI, multimodal models, driven by LLMs, represent a significant leap towards a future where AI can interact with the world in a more nuanced, sophisticated, and human-like manner.
References
- DataCamp, “What is Multimodal AI?” DataCamp Blog, Aug. 28, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.datacamp.com/blog/what-is-multimodal-ai. [Accessed: Aug. 29, 2024].
- Neurons Lab, “Multimodal AI Use Cases: The Next Opportunity in Enterprise AI,” Neurons Lab, Aug. 28, 2023. [Online]. Available: https://www.neurons-lab.com/article/multimodal-ai-use-cases-the-next-opportunity-in-enterprise-ai/. [Accessed: Aug. 29, 2024].
Catch the latest version of this article over on Medium.com. Hit the button below to join our readers there.