What is TinyLlama?
Redefining AI: The Compact Power of TinyLlama in Everyday Applications
Introduction
Imagine a pocket-sized AI that’s as clever as its gigantic cousins. That’s TinyLlama — a new language model challenging the “bigger is better” mantra in artificial intelligence. Despite its small size, TinyLlama can understand and generate text, answer questions, and even help with coding, all while running on everyday devices without the need for distant data centres.
In this article, we delve into the magic behind TinyLlama. We’ll explore how it works, why it matters, and what it could mean for the future of AI. From its innovative training approach to its potential real-world applications, we’ll unpack why TinyLlama is making waves in the AI world.
The Big Picture: AI Language Models
Language models are the digital brains powering AI that understands and generates human-like text. Think of them as hyper-advanced autocomplete systems. These models are trained on vast amounts of text from the internet, books, and articles, learning patterns and relationships between words and ideas. Popular examples like GPT-3 and ChatGPT have made headlines with their ability to write essays, answer questions, and even generate code, showcasing just how far AI has come in understanding and producing human-like text.
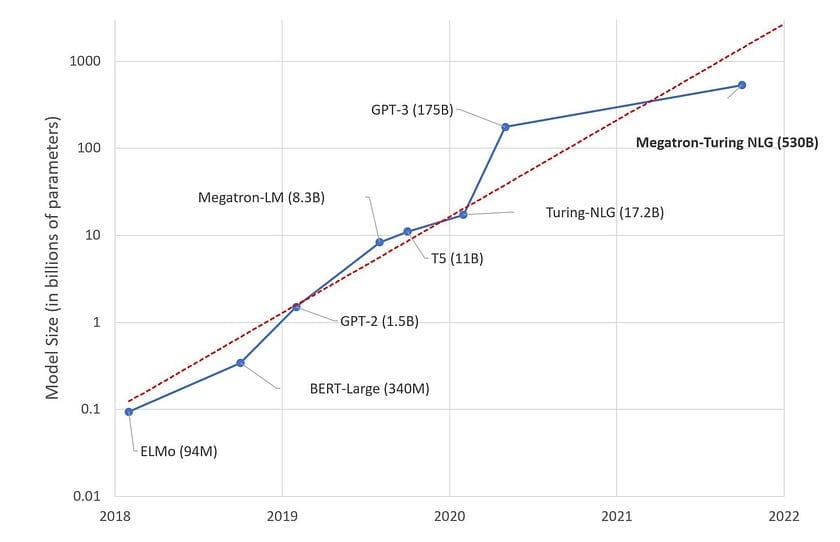
In the world of AI, a clear trend has emerged: bigger is supposedly better. It’s like a digital arms race, with each new model boasting more “knowledge” than the last. GPT-3, released in 2020, wowed the world with its 175 billion parameters. Not to be outdone, Google’s PaLM model came along with 540 billion parameters. Then, in 2023, GPT-4 arrived, with its exact size a closely guarded secret but estimated to be in the trillions. Each leap in size has brought improvements in performance, fueling the belief that to make AI smarter, we just need to make it bigger.
But this “bigger is better” approach comes with significant challenges. These massive models require enormous computing power, comparable to small data centres, just to operate. They’re incredibly expensive to train and run, often consuming as much energy as a small town. Due to their size, they typically need to operate from distant cloud servers, which can lead to slower response times and privacy concerns. It’s like having a brilliant mind that’s too big to fit anywhere except in a massive warehouse — impressive, but not very practical for everyday use.
Enter TinyLlama: The Little Engine That Could
TinyLlama flips the script on the “bigger is better” trend in AI. While it is small in size — just 1.1 billion parameters compared to GPT-3’s 175 billion — it packs a surprising punch. The secret? It’s not about how big you are, but how you train.
What makes TinyLlama stand out is its unique approach. Instead of growing bigger, it focuses on learning better. TinyLlama has only 1.1 billion parameters — a fraction compared to GPT-3’s 175 billion. It’s like comparing a smart, efficient compact car to a massive truck. But here’s the twist: TinyLlama is trained on a whopping 3 trillion tokens (pieces of text), which is more than many larger models. It’s not about having the biggest brain; it’s about reading the most books.
Why “Tiny”? Well, in the world of modern AI, 1.1 billion parameters is indeed tiny. For context, it’s about 0.6% the size of GPT-3 and even smaller compared to the latest models from tech giants. It can run on smaller devices, respond faster, and potentially bring advanced AI capabilities to your smartphone or smart home devices.
Breaking It Down: How TinyLlama Works
TinyLlama’s design is like a miniature version of the famous Llama 2 model, created by Meta (formerly Facebook). It uses the same basic blueprint: imagine a highly sophisticated text prediction engine (that’s the “decoder-only Transformer”) with a special ability to focus on multiple aspects of information simultaneously (that’s the “grouped-query attention”). Think of it as a very smart reader who can not only understand the text but also make connections between different parts efficiently. However, TinyLlama is much more compact. If Llama 2 were a skyscraper with 80 floors and 128 windows on each floor, TinyLlama would be a cozy 22-story building with 32 windows per floor. This similarity in design allows TinyLlama to benefit from Llama 2’s proven effectiveness while being much smaller and more manageable.

The training process of TinyLlama is where its innovation truly shines. The model is exposed to approximately 950 billion tokens from high-quality sources like SlimPajama and Starcoder, with a 7:3 ratio of natural language to code. The training occurs in multiple stages:
- Basic Pre-training: TinyLlama begins with a broad foundation, learning from the diverse SlimPajama dataset. This stage provides the AI with a comprehensive general education across various topics and language patterns.
- Continual Pre-training: Following initial training, TinyLlama undergoes specialised training phases. Different versions focus on specific areas such as mathematical reasoning, coding, or Chinese language processing, akin to an advanced degree program.
- Cooldown Phase: The final stage involves fine-tuning the model’s performance, crucial for consolidating knowledge and improving overall efficiency.
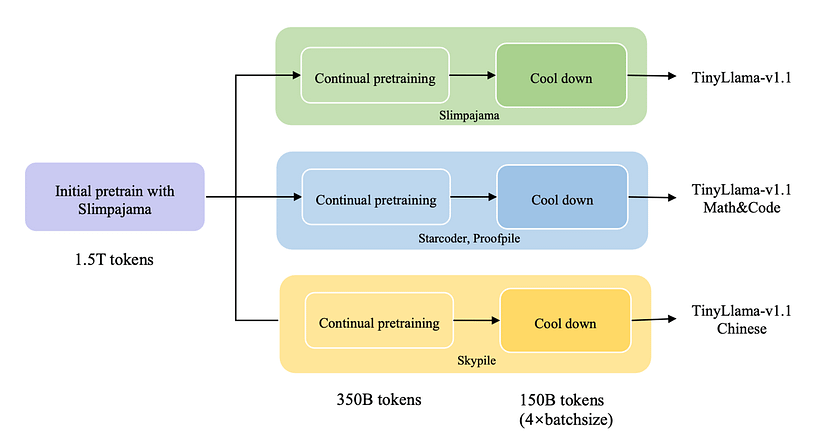
TinyLlama’s success stems from its “quality over quantity” approach to data and training. Rather than simply accumulating vast amounts of information, the model’s creators carefully curated high-quality, diverse datasets. This strategy is analogous to studying in a small, meticulously organised library versus a vast, chaotic warehouse of books. In the well-curated library, like TinyLlama’s training data, relevant and high-quality information is readily accessible, allowing for efficient learning despite the smaller size. This approach demonstrates that in AI, as in education, the quality and structure of learning material can be just as crucial as quantity.
The Benefits of Being Small
TinyLlama’s compact size isn’t just a technical curiosity — it opens up a world of practical advantages. Let’s explore how being small translates into significant benefits:
- Faster Processing: TinyLlama’s smaller size allows it to think on its feet. While larger models might need to ponder for a moment, TinyLlama can often respond in the blink of an eye. In technical terms, it can process about 7,000 tokens (roughly 5,000 words) per second on a single high-end GPU. This speed isn’t just about impatience — it’s crucial for real-time applications like live language translation or interactive AI assistants.
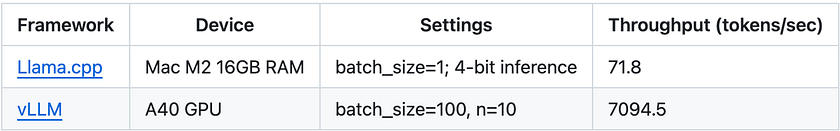
2. Less Resource-Intensive: Big AI models are power-hungry beasts, often requiring energy equivalent to that used by small towns. TinyLlama, in contrast, sips power like a hybrid car. It can run efficiently on a single GPU, making it far more economical to operate. This efficiency extends to memory usage too — while some models need hundreds of gigabytes of RAM, TinyLlama can operate comfortably with much less. For businesses and researchers, this translates to significantly lower operational costs.
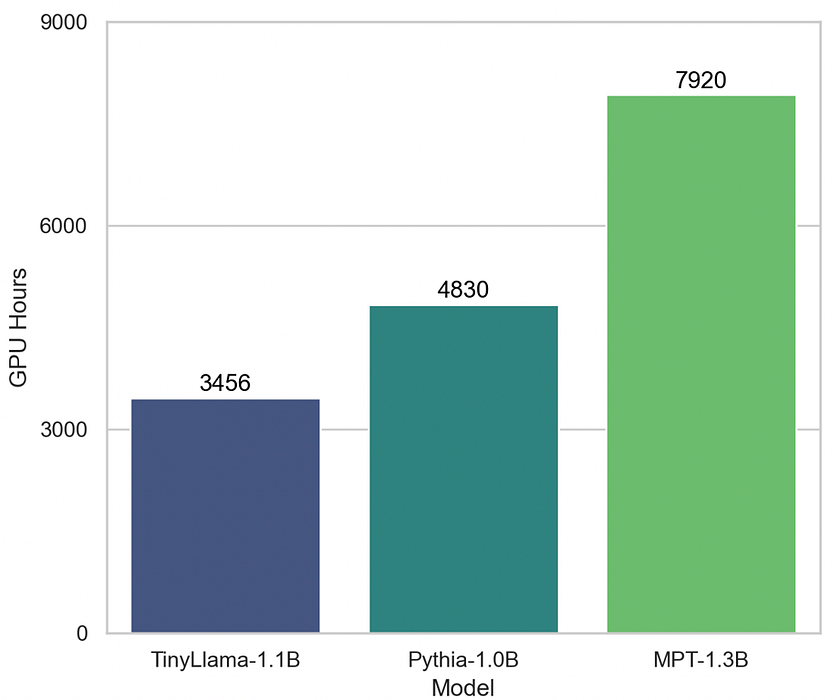
3. Potential for Wider Accessibility: Perhaps the most exciting aspect of TinyLlama is its potential to democratise advanced AI. Its modest hardware requirements mean it could potentially run on devices like smartphones or laptops, bringing cutting-edge AI capabilities directly into users’ hands. Imagine having a powerful AI assistant that works offline, respects your privacy by processing everything locally, and doesn’t drain your battery. This could revolutionise fields like education, where personalised AI tutors could be accessible to students anywhere, anytime.
Real-World Applications
TinyLlama’s compact yet robust framework unlocks numerous possibilities that could transform everyday technology interactions. Imagine having an offline AI assistant integrated into your smartphone, capable of assisting with tasks like writing, coding, or translating languages without draining the battery or infringing on privacy. In education, TinyLlama could support personalized AI tutors that adapt to different learning styles and are accessible anywhere. For businesses, it could power efficient local server-based customer service chatbots, cutting costs and decreasing response times. In the Internet of Things (IoT) sector, TinyLlama could enhance smart home devices with advanced language processing, enabling smoother voice interactions with your appliances. In healthcare, it could provide real-time language translation for telemedicine or drive AI-enhanced diagnostic tools in portable devices. By advancing AI capabilities on edge devices, TinyLlama aims to enrich our gadget functionality, personalise our online interactions, and streamline our engagement with technology.
Challenges and Limitations
Despite its impressive performance, TinyLlama has limitations. It may struggle with complex reasoning tasks, highly specialised domains, or situations requiring extensive world knowledge. Its smaller size means less capacity for information, potentially leading to challenges in multi-step reasoning or expert-level insights. Additionally, its more limited training data could result in blind spots or biases in underrepresented areas.
However, these limitations reflect TinyLlama’s design goals. It’s not meant to replace larger models but to offer an efficient alternative for everyday AI applications. While unsuitable for tasks requiring the highest accuracy, like critical medical diagnoses, TinyLlama’s balance of capability and efficiency opens new possibilities in resource-constrained environments, representing a trade-off between the depth of larger models and increased accessibility.
Conclusion
TinyLlama challenges the “bigger is better” AI paradigm, proving that compact models can deliver impressive performance. While it can’t match the largest models’ breadth, its efficiency opens doors to more accessible AI applications. TinyLlama’s ability to run on smaller devices could democratize AI technology, bringing advanced capabilities to smartphones and IoT devices. This approach may reshape our daily interactions with AI, making sophisticated language models more ubiquitous. TinyLlama’s success demonstrates that AI innovation isn’t just about scale — it’s about finding smarter ways to learn and adapt, potentially ushering in a new era of efficient, accessible AI.
References
[1] Large Language Models — Hugging Face Blog. Read article.
[2] TinyLlama: An Open-Source Small Language Model — GitHub Repository. Explore code.
[3] TinyLlama: An Open-Source Small Language Model — arXiv preprint. Read paper.
[4] TinyLlama: An Open-Source Small Language Model — arXiv HTML version. Read HTML version.
Catch the latest version of this article over on Medium.com. Hit the button below to join our readers there.